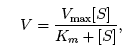Rational Function Applications
Michaelis-Menten Kinetics
Use the Michaelis-Menten equation to answer the following questions: Find the velocity of a reaction given the substrate concentration. Find the substrate concentration given the reaction velocity. Determine the velocity of a reaction as the substrate concentration approaches infinity. ***** |
The Biology Project > Biomath > Rational Functions > Applications > Michaelis-Menten Kinetics
The Biology Project
Department
of Biochemistry and Molecular Biophysics
The University of Arizona
February 2007
Contact the Development Team
http://www.biology.arizona.edu All contents copyright © 2007. All rights reserved.