Make a list of all definitions in the section (a few words each is fine). Summarize any lengthy definitions introduced in this section in your own words.
-
The concept of a limit - denoted, for example, as

which we read as ``the limit of f as x approaches a is L''. It means that the closer x gets to a, the more f(x) tends to the value L (but we don't let x take on the value a). This may be denoted
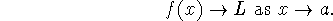
-
One-sided limits: as we see in the examples, a limit may fail to exist as a
whole at a, but exist to one side or the other.
-
left-hand limit:

means that as a is approached from the left (i.e. from values less than a) the function values approach L).
-
right-hand limit:

means that as a is approached from the right (i.e. from values greater than a) the function values approach L).
-
left-hand limit:
-
Infinite limits: our author says that a limit can fail to exist because the
function becomes arbitrarily large (in either a positive or negative sense). In
spite of this fact, the notation used seems to imply that the limit does exist:
-

means that as a is approached from either side, the function gets increasingly large and grows in an unbounded manner.
-

means that as a is approached from either side, the function gets arbitrarily large in a negative sense.
We will say that ``the limit is infinity'', or that ``the limit is negative infinity'', in spite of our author's take on things!
-
-
Vertical asymptote - if a limit is infinity as
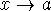 ,
, 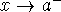 , or
, or 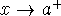 , then the graph will tend toward the vertical line x=a (called a
vertical asymptote to the graph).
, then the graph will tend toward the vertical line x=a (called a
vertical asymptote to the graph).
Make a list of all theorems (lemmas, corollaries) in the section (a few words each is fine). Summarize each one introduced in this section in your own words.
![]()
Make a note of any especially useful properties, tricks, hints, or other materials.
-
It doesn't matter what's actually happening to f at a, in

The limit is only concerned with the behavior of f near a: f(a) could exist or not exist as far as the limit is concerned.
- Example 2 (p. 74) shows that the calculator is not infallible.
- Tabular data (functions defined as tables, for example) do not lend themselves to limits. The idea of limit simply doesn't apply.
Summarize the section in two or three sentences.
We are introduced to the limit in several different flavors: one-sided limits, infinite limits, and the old standby
![]()
The idea is to explore the behavior of the function f as its argument x
gets arbitrarily close to a fixed number a (but x doesn't actually reach
a). f can be smoothly tending towards L, have a jump at L, or could
even be infinite as x approaches a (in which case L would be ![]() ,
leading to a vertical asymptote at x=a).
,
leading to a vertical asymptote at x=a).